BHRINGARAJA
- Home / DRAVYAGUNA (AYURVEDIC PHARMACOLOGY) / / KNOW ABOUT MEDICINAL PLANTS / / AYURVEDIC MEDICINAL PLANTS /
- BHRINGARAJA
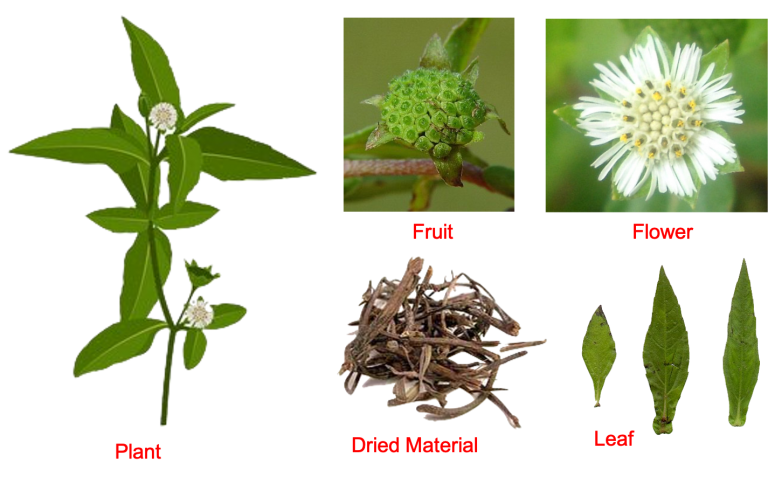
Bhringaraja a plant that is considered to have a wide application in the area of cosmetics especially hair care from time immemorial. Its ability to provide black colour to hair and also nourishment has resulted in its extensive use. The botanical name of the plant is Eclipta alba Hassk and belongs to the family Asteraceae or earlier known as Compositae. The name Eclipta is derived from the greek word ekleipo which means lacking or deficient while the name alba is the latin word for “white” colour. The plant is usually seen throughout India especially near moist places or fields, etc as weeds. The details of the plant are as described below.
PLANT DETAILS
BOTANICAL NAME
FAMILY
Asteraceae
NOMENCLATURE
VERNACULAR NAMES
- Kannada – Garaga
- Malayalam – Tekaraja
- Tamil – Kaikeshi
- Telugu – Galagara
- Hindi – Bhangra
- English – False daisy
SANSKRIT SYNONYMS
- भृङ्ग (Bhringa), भृङ्गराज (Bhringaraja), भृङ्गरज (Bhringaraja) – The ability to attract the bees towards it.
- केशराज (Kesharaja) – A woody part which is tubelike.
- वराहिक (Varahika), वराहकार्णी (Varahakarni) – The leaves are like that of the ears of pig
- तुरगी (Turagi), वाजिनी (Vajini), हयी (Hayi) – The smell of the roots are similar to that of the horse
- वनज (Vanaja) – Sweet taste of the root
- पुष्टिदा (Pushtida), बलद (Balada) – Highly nutritional
- पुण्य (Punya) – The plant is meritorious
- पीवरी (Pivari) – The seeds are flattened in shape.
BRIEF MORPHOLOGY
An annual erect or prostrate herb often branching and rooting at the nodes with appressed white hairs. The leaves are sessile usually oblong-lanceolate with appressed hairs on both sides and base tapering. Inflorescence is head around 6-8mm diameter with two sets of florets. The Ray florets (ray flowers) are white, ligulate spreading, not toothed. Disc florets (Disc flowers) are tubular, with 4 toothed. Fruit is Achenes, black, compressed, with a narrow wing and one seed.
PHARMACOGNOSY OF OFFICIAL PART
MACROSCOPY
YET TO BE COMPILED
MICROSCOPY
YET TO BE COMPILED
PART USED AND POSOLOGY
PART USED
पञ्चाङ्ग (Whole plant), पत्र (Leaves), बीज/फल (Seed/Fruit)
DOSE
चूर्ण (Powder) – 1 to 3 gms, स्वरस (Juice) – 6 to 12 ml
PHYTOCHEMISTRY
The leaves contain Wedelolactone, Leucine, Isoleucine, Valine, Desmethylwedelolactone-7-glycoside, Stigmasterol, Glycine, Glutamine, Glutamic acid, Cystone, Methionine, etc. The roots contain Hentriacontanol, Heptacosanol, Ecliptal, Eclalbatin, etc. The whole plant contains Resin, Ecliptine, Reducing sugar, Nicotine, Stigmasterol, Triterpene saponin, Eclalbatin, Ursolic acid, Oleanolic acid, etc
रसपञ्चक कर्म PROPERTIES AND USES AS PER AYURVEDA
गुण (Properties)
- रस (Rasa) – कटु (Katu), तिक्त (Tikta)
- गुण (Guna) – रूक्ष (Ruksha), लघु (Laghu)
- वीर्य (Veerya) – उष्ण (Ushna)
- विपाक (Vipaka) – कटु (Katu)
- प्रभाव – None
कर्म & प्रयोग (Action & Indications)
- दोषकर्म (Doshakarma) – कफवातशामक (Kaphavatashamaka)
- धातुकर्म & मलकर्म (Dhatukarma and Malakarma) – Main actions – केश्य, त्वच्य, कृमिघ्न, शोथघ्न, दन्त्य, रसायन, बल्य, कुष्ठघ्न & नेत्र्य (Keshya, Twachya, Shothaghna, Dantya, Rasayana, Balya, Kustaghna & Netrya)
- Other Actions – दीपन, पाचन, यकृदुत्तेजक, रक्तप्रसादन, मूत्रल, व्रणशोधन, रेचक, स्वेदजनन & आमपाचन (Deepana, Pachana, Yakriduttejaka, Raktaprasadana, Mutrala, Vranashodhana, Rechaka, Swedajanana & Amapachana)
- प्रयोग (Prayoga) – Mainly कास, श्वास, दन्तरोग, कुष्ठ, नेत्ररोग, शिरोरोग, शौथ & पाण्डु (Kasa, Shwasa, Dantaroga, Kushta, Netraroga, Shiroroga, Shotha & Pandu), also useful in अम्लपित्त, श्लीपद, श्वित्र, कर्णरोग, नासारोग, विसर्प,, विस्फोट, क्लैब्य, उदर्द, शीतपित्त etc (Amlapitta, Shleepada, Shwitra, Karnaroga, Nasaroga, Visarpa, Vishpta, Klaibya, Udarda, Sheetapitta, etc)
AYURVEDIC FORMULATIONS
CLASSICAL
- शड्बिंदु तैल
- नीलभृङ्गादि तैल
- भृङ्गराजासव
- भृङ्गराज तैल
- भृङ्गराजादि चूर्ण
PROPRIETARY
- Bhringamla Hair oil
- Indulekha Hair oil
- Bhringaraj Hair oil
- Trichup Oil & Capsule
AGRONOMY
ENVIRONMENT
The plant grows in variety of soils raning from sandy to clay. But it prefers warm climate with temperature ranging from 25 to 35 deg C, in water logged or damp areas. Red loamy soils rich in organic matter are best for its cultivation. It also grows well in sub-tropic and temperate regions.
CULTIVATION
Saplings can be raised from seed or stem cuttings. But seed is the most preferred one. Freshly collected mature seeds are sown or stem cuttings with 5-6 nodes are planted in nursery beds. They are transplanted into the fields with pits of 30 cms after 45 to 60 days or 4-6 weeks (in case of stem cuttings). The best time to transplant is between April and May. The irrigation is provided twice a week for 1 month, later once a week depending upon rainfall and moisture of the soil. Weeding is to be done every 30-35 days and after each harvest.
HARVESTING
The plants get matured for harvesting in 90 days and at early flowering stage. Harvesting is done by plucking out the plant with roots being chopped. Care should be taken to avoid parts that are affected with fungus.
STORAGE
The parts harvested are cleaned and dried in shade. Upon drying the herbage is packed in gunny bags and stored in cool place. An yield of dried herbage is 2400 kg per acre is obtained.
VARIETIES AND SUBSTITUTES OR ADULTERANTS
VARIETIES
As per Raja Nighantu, it is of three types namely –
- Shweta – Eclipta alba Hassk.
- Peeta – Wedelia calendulacea Less.
- Neela – Eclipta prostrata L.
ADULTERANTS
NONE MENTIONED
SUBSTITUTES
YET TO BE COMPILED
TOXICITY
TOXIC SYMPTOMS
- YET TO BE COMPILED
ANTIDOTE
- YET TO BE COMPILED
शोधन or PURIFICATION METHOD
- YET TO BE COMPILED
THERAPEUTIC USES
EXTERNAL USES –
The fresh leaf juice is applied over the scalp for the purpose of promoting hair growth. Paste of fresh plant is mixed sesame oil and applied over the affected part to treat elephantiasis. The juice of the plant is applied over ulcers or wounds in cattle. Fresh leaf juice is applied over the head to treat dandruff and immature greying of hair. Around 2-5 grams of fresh leaf paste is applied over fresh wounds to facilitate healing.
INTERNAL USES –
The juice of the herb in combination with aromatic herbs are given to children as tonic. For this purpose 2drops of the juice is mixed with 8 drops of honey and given internally. 1 teaspoon of the juice extracted from leaves is given internally to treat Jaundice. To treat Night-blindness, the paste of the plant is given internally along with sugar. Whole plant is ground with black pepper and made into small pills. Two pills are then administered internally to infants to treat Jaundice and Fever.
CONTROVERSY (IF PRESENT)
YET TO BE COMPILED
LIST OF RESEARCH STUDIES
- Chaitra: Bhringaraja – A Beacon for Rejuvenation; ayurpub; IV(6): 1380-1387.
- Jahan, Rownak et al. “Ethnopharmacological Significance of Eclipta alba (L.) Hassk. (Asteraceae).” International scholarly research notices vol. 2014 385969. 29 Oct. 2014, doi:10.1155/2014/385969
- Inseo Kim1, Jee Young Park1, Yun Sun Lee et al. “Discrimination and Authentication of Eclipta prostrata and E. alba Based on the Complete Chloroplast Genomes.” Plant Breeding and Biotechnology 2017 vol. 5. Pg 334-343 Dec. 2017, https://doi.org/10.9787/PBB.2017.5.4.334
- [Krishna priya.A and Shincymol.V.V. (2019); PEETHA BHRINGARAJA [WEDELIA CHINENSIS (OSBECK) MERRILL] – AYURVEDIC LITERARY REVIEW. Int. J. of Adv. Res. 7 (Aug). 500-504] (ISSN 2320-5407). www.journalijar.com